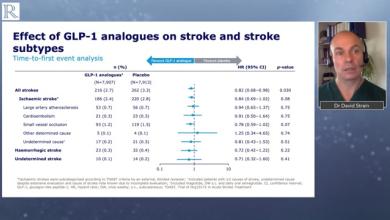
Several clinical and non-clinical risk factors for stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation have been identified, and clinically useful classification schemes have been developed to facilitate risk stratification in these patients.
Both a history of hypertension and systolic blood pressure >160 mmHg have been shown to be consistent independent risk factors for stroke, resulting in a twofold increase in stroke risk.